Overview
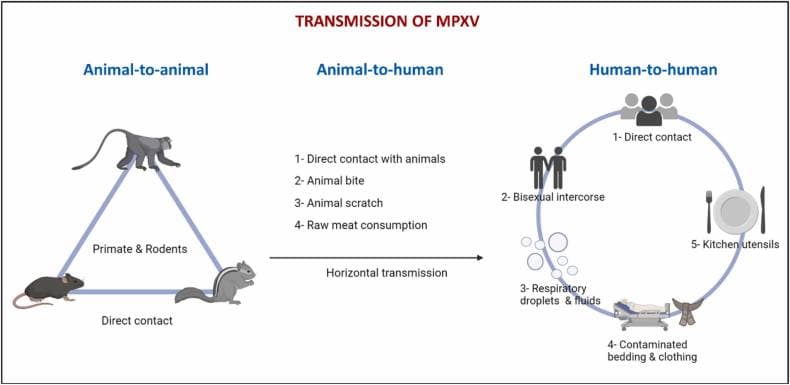
The monkeypox virus (MPXV), abbreviated Mpox, is a zoonotic disease induced by the monkeypox virus of the genus Orthopoxvirus(1,2). Its common transmission is through physical contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated surfaces and is estimated to have a 10% fatality rate. The virus is considered endemic to Africa and occurs naturally in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) (1).
The Mpox genome sequence is dsDNA-based, has roughly 192,200 bases, contains 181 protein-coding genes, and has a highly conserved central region (1,3). The terminal regions are more variable and harbor genes that play roles in determining the range of hosts the virus can infect and the mechanisms causing disease (1).
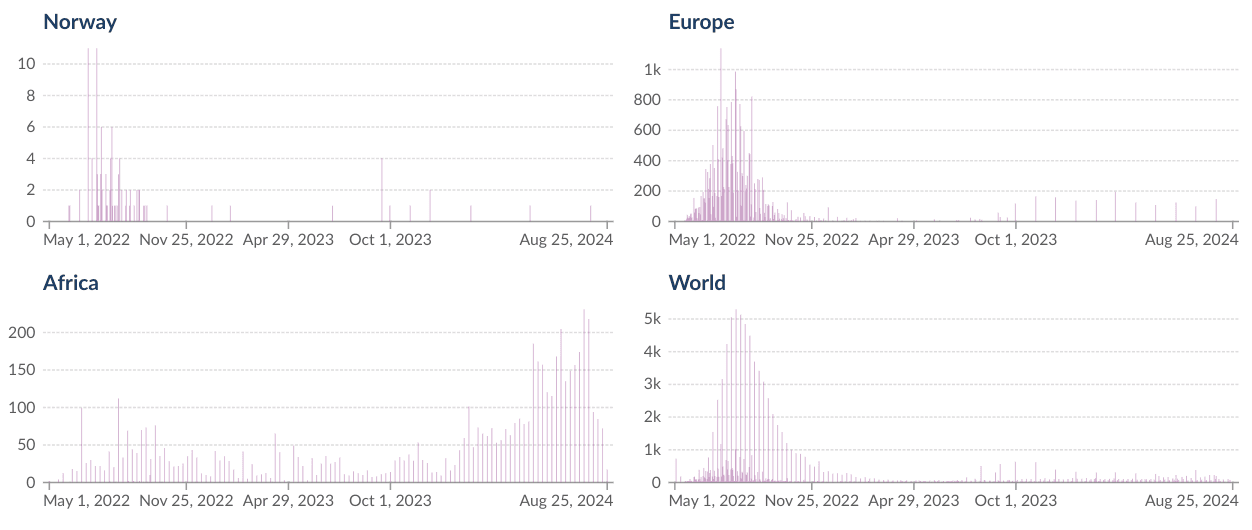
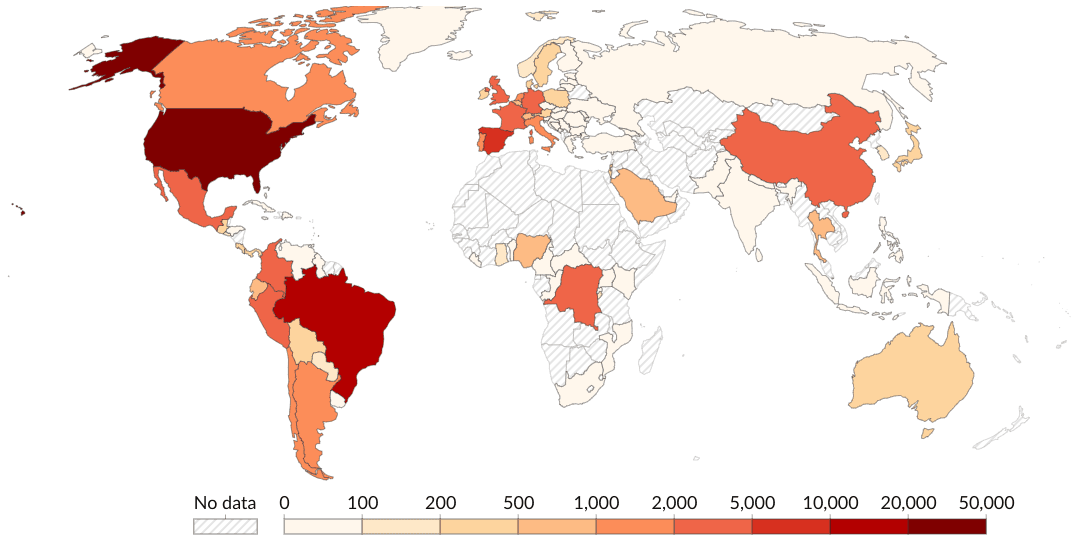
To provide high-value data the Tromsø node of ELIXIR Norway has created a database of 5856 manually curated mpox virus sequences. Metadata for these sequences have been cleaned, standardized, and enriched with fitting ontology terms to better tie the sequence data to available contextual information relating the samples to their origins.
Norwegian resources for Mpox
External Resource
- Latest publication in Cristin
- Ongoing projects listed in Projektbanken


